GD1#
从图标可以推测出是用Godot引擎开发的游戏
使用 gdsdecomp 工具解包并反编译 GDScript 脚本
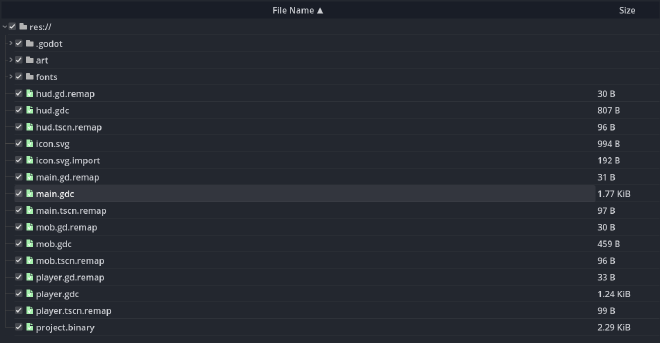

几乎就是源码了,没有混淆,可读性很好。加密只是简单的进制编码
扔给AI写个脚本,python还原逻辑得到flag
a = "000001101000000001100101000010000011000001100111000010000100000001110000000100100011000100100000000001100111000100010111000001100110000100000101000001110000000010001001000100010100000001000101000100010111000001010011000010010111000010000000000001010000000001000101000010000001000100000110000100010101000100010010000001110101000100000111000001000101000100010100000100000100000001001000000001110110000001111001000001000101000100011001000001010111000010000111000010010000000001010110000001101000000100000001000010000011000100100101"
result = ""
# 每次取12位
for i in range(0, len(a), 12):
bin_chunk = a[i:i+12]
if len(bin_chunk) < 12:
break # 确保长度足够
# 分割为三部分:各4位
hundreds_bin = bin_chunk[0:4] # 百位
tens_bin = bin_chunk[4:8] # 十位
units_bin = bin_chunk[8:12] # 个位
# 转为整数
hundreds = int(hundreds_bin, 2)
tens = int(tens_bin, 2)
units = int(units_bin, 2)
ascii_value = hundreds * 100 + tens * 10 + units
result += chr(ascii_value)
# 输出结果
print("Result:", result)
#Result: DASCTF{xCuBiFYr-u5aP2-QjspKk-rh0LO-w9WZ8DeS}
PLUS#
Python3.9,导入init.pyd里面的东西看一下,用到了unicorn和methodcaller之类,大概是vm
不执行指令,单独hook一下参数
from init import *
def null_emu(*args, **kwargs):
return b'0'
class Hook_m():
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
print(f"methodcaller {args} {kwargs}")
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
pass
m = Hook_m
b = null_emu
# encrypt = exec(exit('''int(3 + 4 + ...) + ...'''))
# print("enc = ",encrypt)
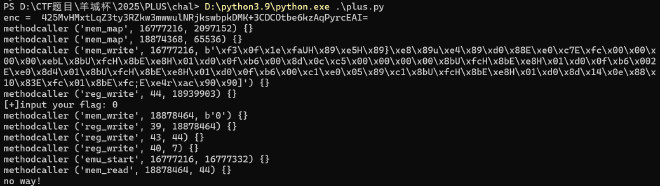
还原一下调用流程
from unicorn import Uc, UC_ARCH_X86, UC_MODE_64, UC_PROT_READ, UC_PROT_WRITE, UC_PROT_EXEC
from unicorn.x86_const import *
user_input = input()
uc = Uc(UC_ARCH_X86, UC_MODE_64)
uc.mem_map(0x1000000, 0x200000) # 代码区
uc.mem_map(0x1200000, 0x10000) # 数据区
code = b'\xf3\x0f\x1e\xfaUH\x89\xe5H\x89}\xe8\x89u\xe4\x89\xd0\x88E\xe0\xc7E\xfc\x00\x00\x00\x00\xebL\x8bU\xfcH\x8bE\xe8H\x01\xd0\x0f\xb6\x00\x8d\x0c\xc5\x00\x00\x00\x00\x8bU\xfcH\x8bE\xe8H\x01\xd0\x0f\xb6\x002E\xe0\x8d4\x01\x8bU\xfcH\x8bE\xe8H\x01\xd0\x0f\xb6\x00\xc1\xe0\x05\x89\xc1\x8bU\xfcH\x8bE\xe8H\x01\xd0\x8d\x14\x0e\x88\x10\x83E\xfc\x01\x8bE\xfc;E\xe4r\xac\x90\x90]'
enc = '425MvHMxtLqZ3ty3RZkw3mwwulNRjkswbpkDMK+3CDCOtbe6kzAqPyrcEAI='
uc.mem_write(0x1000000, code)
uc.mem_write(0x1201000, user_input)
uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RSP, 0x120ffff)
uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RDI, 0x1201000)
uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RSI, 44)
uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RDX, 7)
try:
uc.emu_start(0x1000000, 0x1000074)
result = uc.mem_read(0x1201000, 44)
except Exception as e:
pass
刚好模拟执行的是Intel x86的机器码,直接十六进制写到bin文件里,然后扔进ida反编译
加密是单字节的线性运算,爆破即可

import base64
digist_table = b"0123456789"
lower_table = b"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
supper_table = b"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
punct_table = b"!\"#$%&\'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}"
brute_table = digist_table + lower_table + supper_table + punct_table
enc = '425MvHMxtLqZ3ty3RZkw3mwwulNRjkswbpkDMK+3CDCOtbe6kzAqPyrcEAI='
enc_list = list(base64.b64decode(enc))
def encrypt(byte):
res = ((byte * 8) + (byte ^ 7) + (byte << 5)) & 0xff
return res
for index in range(0,44):
for ch in brute_table:
check = encrypt(ch)
if check == enc_list[index]:
print(chr(ch),end="")
ez_py#
题目一共给出2个待分析文件,一个是PyInstaller打包的exe文件,另一个是受pyarmor加密混淆的src.py
先分析key.exe,pyinstxtractor解包拿到pyc,进一步反编译。
首先尝试使用pycdc进行反编译,但是报错相当严重。改用在线的PyLingual能还原出完整代码,但是反编译过程中也对原始bytecode做了很多patch,而且仍然存在语法错误

对于报错的Phrolova函数,直接用pycdas取出对应部分的bytecode,交给deepseek重新反编译。
def Phrolova(o0o0o17):
o0oA = 'Carlotta'
o0oB = ['o0oC', 'o0oD', 'o0oE', 'o0oF']
o0oG = []
o0oG.append(ast.Assign(targets=[ast.Name(id='o0oH', ctx=ast.Store())],value=ast.Constant(305419896)))
o0oG.append(ast.Assign(targets=[ast.Name(id='o0oI', ctx=ast.Store())],value=ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oE', ctx=ast.Load()), ast.BitAnd(),ast.Constant(65535))))
o0oG.append(ast.Assign(targets=[ast.Name(id='o0oJ', ctx=ast.Store())],value=ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oE', ctx=ast.Load()), ast.RShift(),ast.Constant(16)), ast.BitAnd(), ast.Constant(65535))))
o0oG.append(ast.Assign(targets=[ast.Name(id='o0oK', ctx=ast.Store())],value=ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oE', ctx=ast.Load()), ast.BitXor(),ast.Name(id='o0oF', ctx=ast.Load())), ast.BitAnd(), ast.Constant(65535))))
o0oG.append(ast.Assign(targets=[ast.Name(id='o0oL', ctx=ast.Store())],value=ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oE', ctx=ast.Load()),ast.RShift(), ast.Constant(8)), ast.BitXor(), ast.Name(id='o0oF',ctx=ast.Load())), ast.BitAnd(), ast.Constant(65535))))
o0oG.append(ast.Assign(targets=[ast.Name(id='o0oM', ctx=ast.Store())],value=ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oH', ctx=ast.Load()), ast.Mult(),ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oF', ctx=ast.Load()), ast.Add(), ast.Constant(1))),ast.BitAnd(), ast.Constant(4294967295))))
o0oG.append(ast.Assign(targets=[ast.Name(id='o0oN', ctx=ast.Store())],value=ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oD',ctx=ast.Load()), ast.LShift(), ast.Constant(5)), ast.Add(), ast.Name(id='o0oI',ctx=ast.Load())), ast.BitXor(), ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oD', ctx=ast.Load()),ast.Add(), ast.Name(id='o0oM', ctx=ast.Load()))), ast.BitXor(),ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oD', ctx=ast.Load()), ast.RShift(),ast.Constant(5)), ast.Add(), ast.Name(id='o0oJ', ctx=ast.Load())))))
o0oG.append(ast.Assign(targets=[ast.Name(id='o0oP', ctx=ast.Store())],value=ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oC', ctx=ast.Load()), ast.Add(),ast.Name(id='o0oN', ctx=ast.Load())), ast.BitAnd(), ast.Constant(65535))))
o0oG.append(ast.Assign(targets=[ast.Name(id='o0oN', ctx=ast.Store())],value=ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oP',ctx=ast.Load()), ast.LShift(), ast.Constant(5)), ast.Add(), ast.Name(id='o0oK',ctx=ast.Load())), ast.BitXor(), ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oP', ctx=ast.Load()),ast.Add(), ast.Name(id='o0oM', ctx=ast.Load()))), ast.BitXor(),ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oP', ctx=ast.Load()), ast.RShift(),ast.Constant(5)), ast.Add(), ast.Name(id='o0oL', ctx=ast.Load())))))
o0oG.append(ast.Assign(targets=[ast.Name(id='o0oQ', ctx=ast.Store())],value=ast.BinOp(ast.BinOp(ast.Name(id='o0oD', ctx=ast.Load()), ast.Add(),ast.Name(id='o0oN', ctx=ast.Load())), ast.BitAnd(), ast.Constant(65535))))
o0oG.append(ast.Return(ast.Tuple(elts=[ast.Name(id='o0oP', ctx=ast.Load()),ast.Name(id='o0oQ', ctx=ast.Load())], ctx=ast.Load())))
o0oU = ast.FunctionDef(name=o0oA, args=ast.arguments(posonlyargs=[], args=[ast.arg(arg=a) for a in o0oB], kwonlyargs=[], kw_defaults=[], defaults=[]),body=o0oG, decorator_list=[])
o0oV = ast.parse('\ndef _tea_helper_func(a, b, c):\n magic1 = (a ^ b) &0xDEADBEEF\n magic2 = (c << 3) | (a >> 5)\n return (magic1 + magic2 - (b &0xCAFEBABE)) & 0xFFFFFFFF\n\ndef _fake_tea_round(x, y):\n return ((x *0x9E3779B9) ^ (y + 0x12345678)) & 0xFFFFFFFF\n\n_tea_magic_delta = 0x9E3779B9 ^0x12345678\n_tea_dummy_keys = [0x1111, 0x2222, 0x3333, 0x4444]\n').body
o0oW = ast.Module(body=[o0oU] + o0oV, type_ignores=[])
ast.fix_missing_locations(o0oW)
o0oX = compile(o0oW, filename='<tea_obf_ast>', mode='exec')
# print(dis.dis(o0oX))
o0oY = {}
exec(o0oX, o0oY)
if o0oA in o0oY:
o0o0o17[o0oA] = o0oY[o0oA]
return None
之后发现Phrolova函数使用ast模块动态编译了另一个函数Carlotta,不能静态看到其逻辑。考虑运行时使用dis.dis输出codetype对象的反编译结果
代码中还有对变量名的混淆,通过查找替换可以批量重命名
梳理出加密流程:shouan -> Carlotta -> changli。两个加密都是变种TEA,细节上略有不同
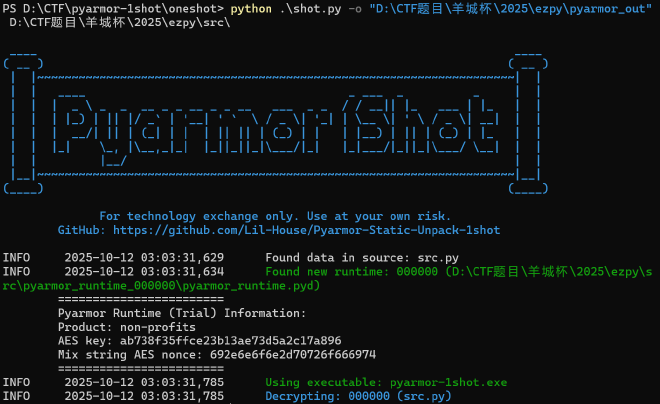
继续分析pyarmor
pyarmor-1shot进行解包,一开始提示找不到data,试了下在bytecode前面加上PY000000就能识别了。
def init(key, key_len):
'__pyarmor_enter_54746__(...)'
i = 0
sbox = None(list, None(range, 256))
for j in None(range, 256):
i = (i + sbox[j] + key[j % key_len]) % 256
sbox[j], sbox[i] = sbox[i], sbox[j]
'__pyarmor_exit_54747__(...)'
return sbox
def make(box):
'__pyarmor_enter_54749__(...)'
i = 0
j = 0
reslut = []
for count in None(range, 256):
i = (i + 1) % 256
j = (j + box[i]) % 256
box[i], box[j] = box[j], box[i]
k = (box[i] + box[j] + count % 23) % 256
reslut.append(box[k])
'__pyarmor_exit_54750__(...)'
return reslut
只有两个函数,一眼看出是RC4,但是稍有魔改。
加密流程在make.__doc__,需要用到前面key.exe验证的key。先解出key再解rc4
from ctypes import *
def spilt_word(num):
high_word = num >> 16
low_word = num & 0xffff
return (high_word, low_word)
def combine_word(high_word, low_word):
return high_word << 16 | low_word
def tea_decrypt(d1,d2,key):
delta = 0x87456123
d1 = c_uint32(d1)
d2 = c_uint32(d2)
k0 = key & 0xffffffff
k1 = (key >> 8 ^ 0x12345678) & 0xffffffff
k2 = (key << 4 ^ 0x87654321) & 0xffffffff
k3 = (key >> 12 ^ 0xabcdef00) & 0xffffffff
number = c_uint32(delta * 32)
for i in range(32):
d2.value -= ((d1.value<<4) + k2) ^ ((d1.value>>4) + k3) ^ (d1.value + number.value)
d1.value -= ((d2.value<<4) + k0) ^ ((d2.value>>4) + k1) ^ (d2.value + number.value)
number.value -= delta
return d1.value,d2.value
def ast_dec(high, low, e, f):
delta = 0x12345678
high = c_uint16(high)
low = c_uint16(low)
k0 = e & 0xffff
k1 = (e >> 16) & 0xffff
k2 = (e ^ f) & 0xffff
k3 = ((e >> 8 ^ f)) & 0xffff
sum = (delta * (f+1)) & 0xffffffff
low.value -= ((high.value<<5) + k2) ^ ((high.value>>5) + k3) ^ (high.value + sum)
high.value -= ((low.value<<5) + k0) ^ ((low.value>>5) + k1) ^ (low.value + sum)
return (high.value, low.value)
def key_dec(key_data):
key = []
for i in range(8,0,-1):
key_data[i-1], key_data[i] = tea_decrypt(
key_data[i-1], key_data[i], 2025
)
for id, word in enumerate(key_data):
magic = id * id
high,low = spilt_word(word)
high,low = ast_dec(high, low, id+2025, magic)
key.append(combine_word(high,low))
print(f"key: {key}")
return key
def RC4_crypt(data,key,origin_key):
length = len(key)
S = [m for m in range(256)]
T = [key[n % length] for n in range(256)]
j = 0
for i in range(256):
j = (j + S[i] + T[i]) % 256
S[i],S[j] = S[j],S[i]
i = j = t = 0
for k in range(len(data)):
i = (i + 1) % 256
j = (j + S[i]) % 256
if k % 2 == 0:
add_key = origin_key[k % 9]
else:
add_key = (origin_key[k % 9] * 2) % 0xFFF
t = (S[i] + S[j] + k % 23) % 256
S[i],S[j] = S[j],S[i]
data[k] ^= S[t] + add_key
return data
key_list = [105084753, 3212558540, 351342182, 844102737, 2002504052, 356536456, 2463183122, 615034880, 1156203296]
cipher = [1473, 3419, 9156, 1267, 9185, 2823, 7945, 618, 7036, 2479, 5791, 1945, 4639, 1548, 3634, 3502, 2433, 1407, 1263, 3354, 9274, 1085, 8851, 3022, 8031, 734, 6869, 2644, 5798, 1862, 4745, 1554, 3523, 3631, 2512, 1499, 1221, 3226, 9237]
origin_key = key_dec(key_list)
rc4_key = [i % 0xff for i in origin_key]
flag = RC4_crypt(cipher,rc4_key,origin_key)
print(bytes(flag))
#key: [1234, 5678, 9123, 4567, 8912, 3456, 7891, 2345, 6789]
#b'flag{8561a-852sad-7561b-asd-4896-qwx56}'
easyTauri#
2048小游戏,但是手太笨了玩不到2048,所以直接逆。
先解包,拿到前端的js文件。逐个分析,关键逻辑在html_actuator.js
去混淆,看出是一个RC4
(function (a, c) {
const d = b;
const e = a();
while (true) {
try {
const a = parseInt(d(176)) / 1 + parseInt(d(172)) / 2 + parseInt(d(170)) / 3 + -parseInt(d(171)) / 4 + -parseInt(d(167)) / 5 * (parseInt(d(168)) / 6) + -parseInt(d(174)) / 7 * (-parseInt(d(166)) / 8) + -parseInt(d(173)) / 9;
if (a === c) {
break;
} else {
e.push(e.shift());
}
} catch (a) {
e.push(e.shift());
}
}
})(c, 452532);
function a(a, c) {
const d = b;
const e = new TextEncoder()[d(169)](a);
const f = new TextEncoder()[d(169)](c);
const g = new Uint8Array(256);
let h = 0;
for (let b = 0; b < 256; b++) {
g[b] = b;
h = (h + g[b] + e[b % e[d(175)]]) % 256;
[g[b], g[h]] = [g[h], g[b]];
}
let i = 0;
let j = 0;
const k = new Uint8Array(f[d(175)]);
for (let b = 0; b < f[d(175)]; b++) {
i = (i + 1) % 256;
j = (j + g[i]) % 256;
[g[i], g[j]] = [g[j], g[i]];
const a = (g[i] + g[j]) % 256;
k[b] = f[b] ^ g[a];
}
return k;
}
function b(a, d) {
const e = c();
b = function (a, b) {
a = a - 166;
let c = e[a];
return c;
};
return b(a, d);
}
function c() {
const a = ["3283052tzDAvB", "542866JdmzNj", "4112658rTyTXQ", "16954tUYpad", "length", "457163LwGIuU", "2696pusaTH", "233035azfeoA", "66oGYEyB", "encode", "2094372kZRrIa"];
c = function () {
return a;
};
return c();
}
在Console先跑一下加密函数,提取密钥流
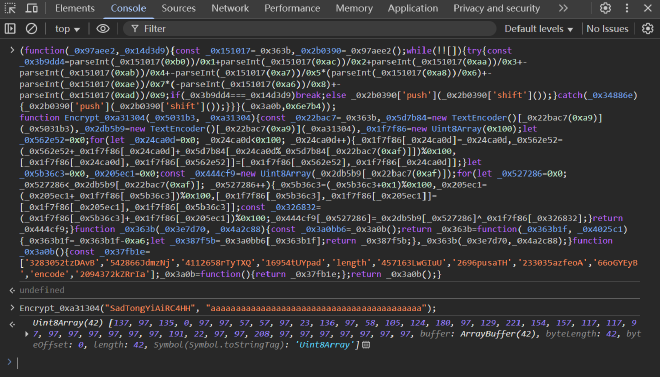
继续找后端的实现。注意到混淆后面的代码提到invoke ipc_command
async function _0x9a2c6e7() {
greetInputEl = document.querySelector("#greet-input");
greetMsgEl = document.querySelector("#greet-msg");
let getFlag = greetInputEl.value;
const ciphertext = Encrypt_0xa31304("SadTongYiAiRC4HH", getFlag);
greetMsgEl.textContent = await invoke("ipc_command", { name: uint8ArrayToBase64(ciphertext) });
}
window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", () => {
document.getElementById("check-form").addEventListener("submit", (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
_0x9a2c6e7();
});
});
去IDA中查找,能找到一样的字符串。紧挨着还有一个可疑的Base64字符串,判断是密文
交叉引用,进一步定位到后端rust函数
具体逻辑是:魔改TEA -> 标准base64 -> 比较密文
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
char std_table[] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/";
void base64_decode(unsigned char *encoded, char *table, unsigned char *decode)
{
char temp[4] = {0}, chr, *index;
int length = strlen(encoded);
for (int i = 0; i*4 < length; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
chr = encoded[i*4+j];
index = strchr(table,chr);
temp[j] = (index==NULL)? 0: index-table;
}
*(decode + i*3) = (temp[0] << 2) | (temp[1] >> 4);
*(decode + i*3 + 1) = (temp[1] << 4) | (temp[2] >> 2);
*(decode + i*3 + 2) = (temp[2] << 6) | temp[3];
}
//printf("%s",decode);
}
void tea_decry_BE(unsigned int *data, unsigned int *key)
{
unsigned int d1, d2;
unsigned int round = 32;
unsigned int delta = 0x7e3997b7, number = delta * round;
d1 = ((data[0] & 0xFF) << 24) | (((data[0] >> 8) & 0xFF) << 16);
d1 |= (((data[0] >> 16) & 0xFF) << 8) | ((data[0] >> 24) & 0xFF);
d2 = ((data[1] & 0xFF) << 24) | (((data[1] >> 8) & 0xFF) << 16);
d2 |= (((data[1] >> 16) & 0xFF) << 8) | ((data[1] >> 24) & 0xFF);
for (int i = 0; i < round; i++)
{
d2 -= ((d1<<4) + key[2]) ^ ((d1>>5) + key[3]) ^ (d1 + number);
d1 -= ((d2<<4) + key[0]) ^ ((d2>>5) + key[1]) ^ (d2 + number);
number -= delta;
}
data[0] = d1;
data[1] = d2;
}
int main()
{
unsigned char decdata[64];
unsigned char data[] = {
0x75,0xa1,0x7f,0x0e,0x44,0x31,0x8b,0x11,0xa6,0xce,0x7d,0x1a,0x3c,0x55,0xb6,0x13,
0x63,0xe1,0x33,0xc3,0x5a,0x6d,0x1b,0x4b,0x8e,0x9e,0xa9,0x23,0xe7,0x3c,0x4e,0xd6,
0x37,0x58,0xcb,0x8f,0xc5,0xf9,0xef,0x94,0x0b,0x29,0xf5,0xa9,0x6e,0x7f,0xc9,0xe8,
0x67,0x2f,0xd3,0xe9,0x2c,0xfd,0x0c,0x98
};
unsigned int tea_key[] = {
0x636c6557,0x74336d4f,0x73757230,0x55615474
};
unsigned int xor_stream[] = {
137, 97, 135, 0, 97, 97, 57, 57, 97, 23, 136,
97, 58, 105, 124, 180, 97, 129, 221, 154, 157,
117, 117, 97, 97, 97, 97, 97, 97, 97, 191, 22,
97, 97, 208, 97, 97, 97, 97, 97, 97, 97
};
unsigned int *Data = (unsigned int *)data;
for(int i=0;i<7;i++)
{
tea_decry_BE(Data+2*i,tea_key);
}
printf("%s\n",data);
base64_decode(data,std_table,decdata);
for(int j=0;j<42;j++)
{
decdata[j] ^= xor_stream[j] ^ 97;
}
printf("%s\n",decdata);
return 0;
}
